Alright, let’s cut through the noise. You want to rank higher on Google, right? Get more traffic, more leads, more sales? Of course, you do. But here’s the deal: you’re not operating in a vacuum. Other businesses are fighting for the same eyeballs, the same clicks, the same customers.
Ignoring them is like trying to win a race without knowing who else is running. That’s where SEO competitor analysis comes in. It’s not about copying; it’s about understanding the battlefield so you can outsmart, outmaneuver, and ultimately, outrank the competition.
Forget the dry theory. This is your battle plan, straight from the trenches, showing you what actually works. We’ll cover exactly how to do competitor analysis in SEO, find actionable insights, and turn them into real growth for your business. Forget the fluff; let’s get results.
What Is SEO Competitor Analysis?
Simply put, SEO competitor analysis is the process of digging into the websites that are currently ranking for the keywords you want to rank for. You’re essentially reverse-engineering their success.
It involves looking at:
- Who your actual search competitors are (they might not be who you think).
- What keywords they’re targeting and ranking for.
- How they structure their content and what topics they cover.
- Where they’re getting their backlinks from.
- Why Google seems to favor their technical setup and user experience.
It’s about gathering intel to inform your own SEO strategy, find shortcuts to success, and avoid reinventing the wheel.
Why Is SEO Competitor Analysis Essential for Growth?
Think of it this way: ignoring your SEO competitors is like driving blindfolded. You might eventually get somewhere, but chances are you’ll crash and burn or end up miles off course. Here’s why making this a core part of your strategy is non-negotiable:
- Discover What’s Actually Working: See which keywords, content types, and link-building tactics are already winning in your niche. Why guess when you can learn from proven success (and failures)?
- Identify Realistic Keyword Targets: Find keywords your competitors rank for that you might have missed. This includes understanding keyword difficulty and finding achievable quick wins.
- Uncover Content Gaps & Opportunities: See what topics your competitors cover that you don’t, or where their content is weak, outdated, or just plain boring. This is gold for your content calendar. An seo content gap analysis is crucial here.
- Benchmark Your Performance: Understand where you stand in terms of traffic, rankings, and authority compared to others. It helps set realistic goals and track progress.
- Refine Your Link-Building Strategy: See who links to your competitors. If a site links to two or three of them but not you, that’s a prime outreach target. Hello, backlink competitor analysis.
- Improve Technical SEO & UX: Identify technical advantages competitors might have (like faster site speed or better mobile experience) that you need to match or beat.
- Stay Ahead of the Curve: See shifts in competitor strategies early, allowing you to adapt proactively instead of reactively.
Bottom line: Competitor analysis gives you a roadmap based on real-world data, saving you time, money, and a hell of a lot of frustration.
Core Steps of SEO Competitor Analysis
Ready to roll up your sleeves? Here’s the step-by-step process. We’ll break down each one.
Step 1: Identify Your True Search Competitors
First things first: your business competitors aren’t always your search competitors. The local pizza shop down the street might be your business rival, but your search competitors could be national chains, recipe blogs, or review sites dominating the results for “best pizza near me.”
How to Find Them:
- Brainstorm Keywords: List the core keywords and phrases your ideal customers would use to find your products or services. Think like them.
For Brainstorming keywords with AI help, here’s a comprehensive prompt.
Make sure you replace everything inside brackets [ ]. 😉
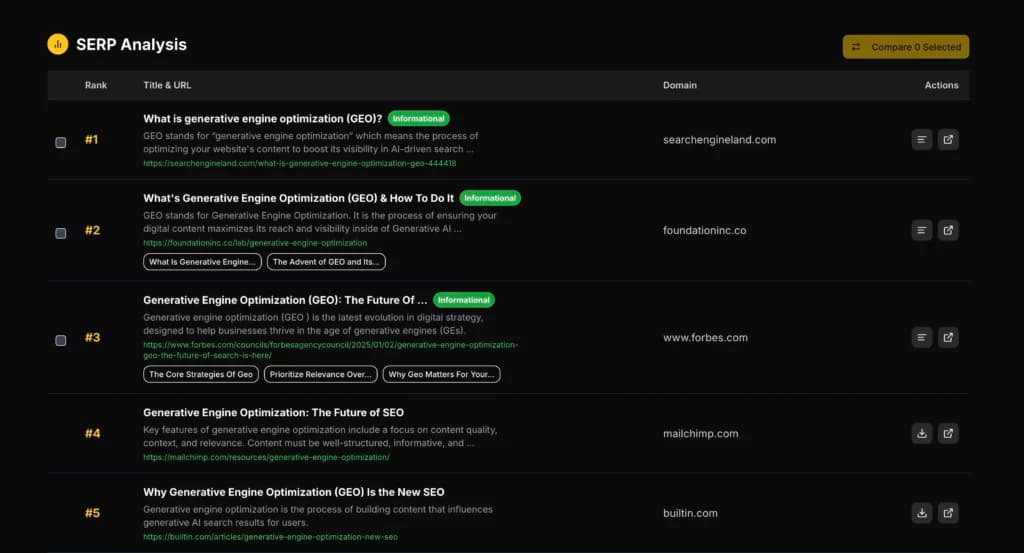
- Use a Keyword Tool to Identify Competitors: Search for your core keywords using TSH’s free keyword research tool. See who consistently shows up on the first page. These are your primary search competitors for those terms.
Our free keyword research tool can help you identify your top competitors very quickly.
- Go to https://theseohustler.com/advanced-keyword-analysis
- Input your keyword
- In the results page, scroll down to SERP Analysis
- Take note of your competitors
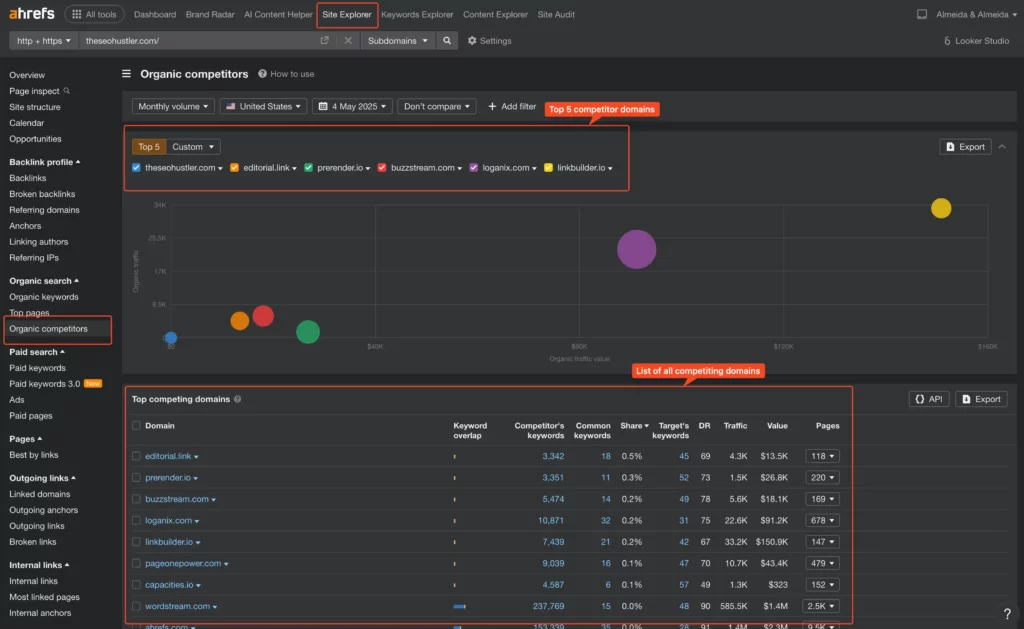
- Use SEO Tools: Tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, or SERanking have features specifically for identifying organic competitors. Input your domain, and they’ll show you sites that rank for a similar set of keywords.
On Ahrefs, click on “Site Explorer” at the top, input your domain and search, then click on “Organic Competitors” on the left sidebar.
- Look Beyond Direct Rivals: Don’t just focus on businesses selling the exact same thing. Consider informational sites, review platforms, directories, and major publications ranking for your terms.
Action: Make a list of your top 3-5 true search competitors for your most important keyword clusters. These are the sites you’ll be dissecting.
Step 2: Analyze Competitors’ Keyword Strategies
Now that you know who you’re up against, let’s figure out what they’re ranking for. This is competitor keyword analysis.
What to Look For:
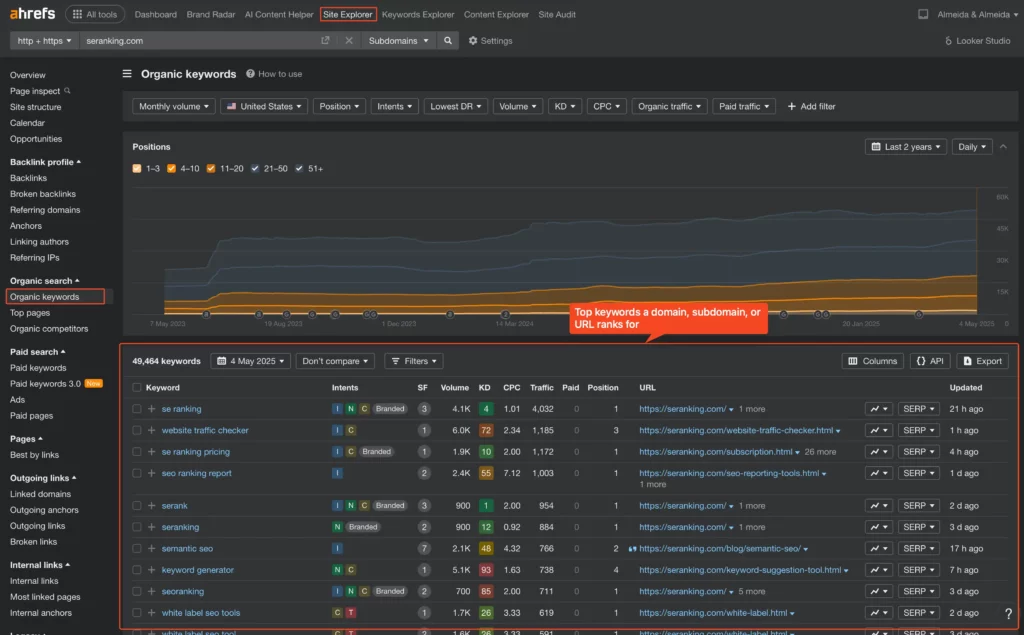
- Top Organic Keywords: Use SEO tools (Semrush’s Organic Research, Ahrefs’ Site Explorer) to see the keywords driving the most traffic to your competitors’ sites.
On Ahrefs, go to “Site Explorer”, then “Organic Keywords” on the sidebar.
- Keyword Gap Analysis: This is HUGE. Identify keywords your competitors rank for (especially multiple competitors) that you don’t. Tools have dedicated “Keyword Gap” or “Content Gap” features for this. These are immediate opportunities.
On Ahrefs, go to “All Tools”, then “Competitive Anlaysis”, then “Content Gap” in the sidebar
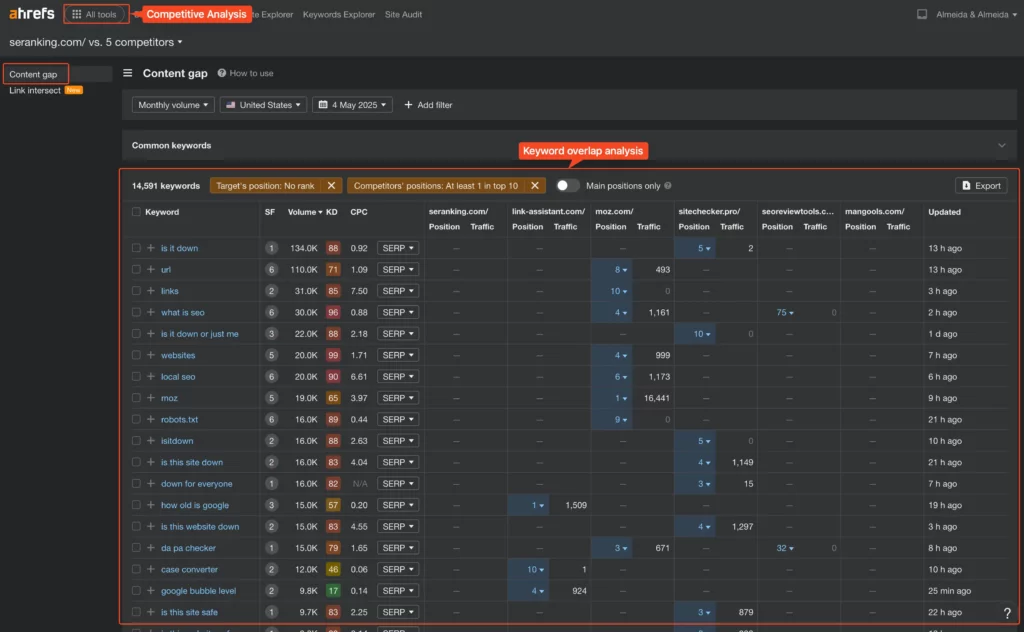
- Ranking Positions & Traffic: See which keywords they rank highly for (positions 1-10) and take note of the traffic these keywords bring. Focus on high-value, relevant terms, this include medium-volume, low-competition keywords, and bottom of the funnel keywords.
- Keyword Intent: Are they targeting informational keywords (“how to fix a leaky faucet”) or transactional ones (“buy tankless water heater”)? Understanding the intent behind their target keywords helps you align your own content. Tools like Ahrefs and SEMRush gives you this information. You can also use our Free Keyword Research Tool for a more comprehensive intent and user needs analysis.
Keyword intent analysis can also be performed with the help of AI, here’s a prompt you can use.
Action: Get that spreadsheet going! List their winning keywords, rankings, traffic estimates, and pinpoint those juicy keyword gaps you can steal.
Step 3: Uncover Content Gaps and Opportunities
Keywords tell part of the story; content tells the rest. You need to understand how competitors are using content to rank for those keywords. This is where seo content gap analysis shines.
How to Analyze:
- Top Performing Content: Use tools (like Ahrefs’ Top Pages or Semrush’s Organic Research Pages) to see which specific pages/posts on competitor sites get the most organic traffic. What topics are they covering? What format is the content (blog post, guide, tool, video)?
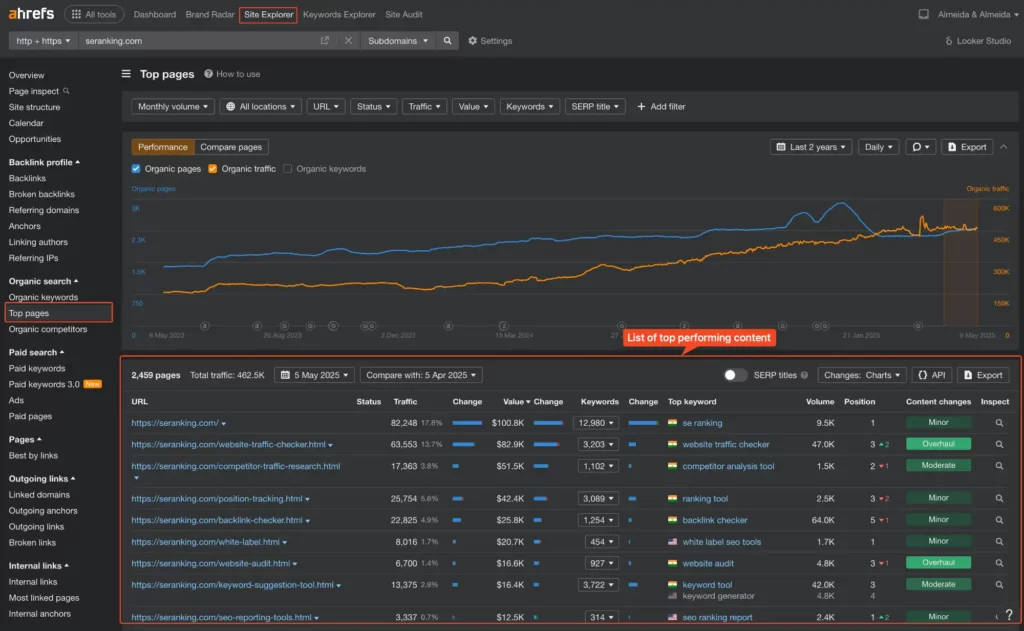
- Content Format & Quality: Manually review their top pages. Are they long-form guides? Short blog posts? Do they use lots of images or videos? Is the content comprehensive, well-written, and genuinely helpful? Or is it thin, outdated, or just keyword-stuffed?
Here’s a prompt to help you in this process:
- Identify Topic Clusters: Do they have multiple pieces of content covering different angles of a broader topic? This “topic cluster” approach signals authority to Google.
- Find Your Gaps: Compare their successful content topics and formats against your own. What are they covering that you aren’t? Where is their content clearly superior (or weaker) than yours?
💡 Expert Tip: You can use Grok3 or another good reasoning after you have collected data from your competitors. It can generate Venn diagrams and more complex analysis for you. Use the prompt below:
Action: List content topics and formats that are working for competitors but missing from your site. Prioritize creating content that fills these gaps or significantly improves upon what they offer (think 10x better).
Step 4: Evaluate Technical SEO & UX Gaps
You could have the best content in the world, but if your site is slow, broken, or a nightmare to use, Google won’t rank it well. Analyzing your competitors’ technical health and user experience (UX) can reveal critical advantages or weaknesses.
What to Check:
- Site Speed & Core Web Vitals: Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights to test your competitors’ key pages (homepage, top content pages). How do they score on metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)? Compare this to your own site.
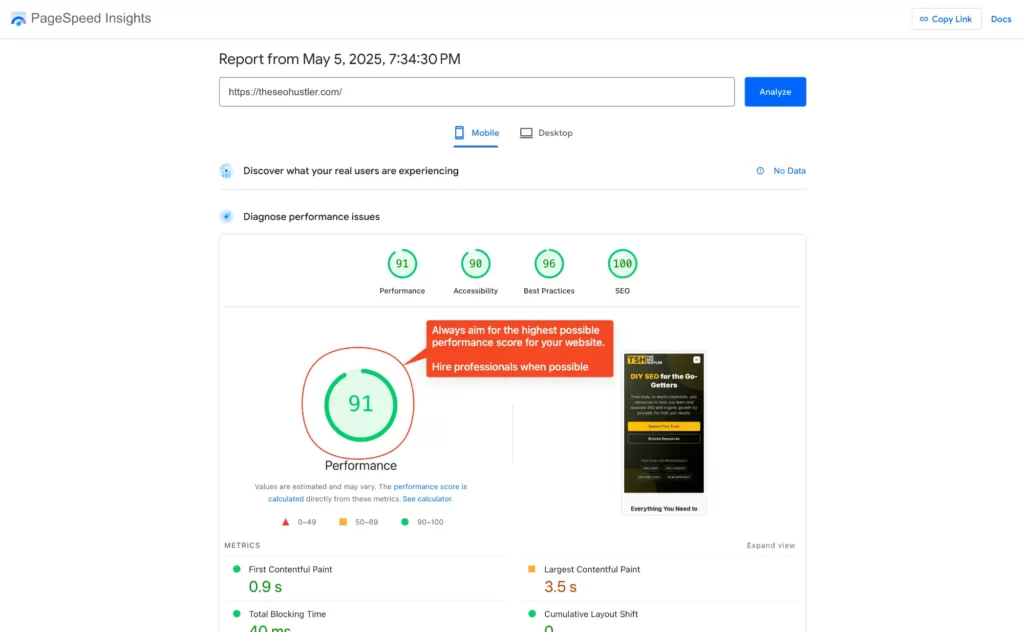
- Mobile-Friendliness: Is their site fully responsive and easy to use on a smartphone? Test it yourself or use SERanking’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
- Site Structure & Navigation: Is their site easy to navigate? Is the structure logical? Can users (and search engines) easily find important pages?
- HTTPS Security: Are they using HTTPS? (They absolutely should be).
- Schema Markup: Are they using structured data (schema) to help Google understand their content and potentially gain rich snippets in search results? Use the Schema Markup Validator.
- Overall User Experience (UX): Browse their site. Is it clean and modern, or cluttered and dated? Are there annoying pop-ups? Does it feel trustworthy and professional?
💡 Pro Tip: Most of those checks can be performed using our on-page analysis tool here.
Action: Identify areas where competitors excel technically or in UX. Use this to prioritize improvements on your own site. If their site speed sucks, that’s an opportunity for you to win. Use technical seo audit tools for deeper dives if needed.
Step 5: Examine Backlink Profiles and Link-Building Tactics
Backlinks are still a massive ranking factor. Understanding who links to your competitors is key to building your own site’s authority. Time for backlink competitor analysis.
How to Do It:
- Use Backlink Tools: Tools like Ahrefs, Moz Link Explorer, or Semrush Backlink Analytics are essential here. Enter your competitors’ domains.
- Analyze Referring Domains: Look at the domains linking to them. Are they high-authority, relevant sites in your industry, or low-quality spam? Focus on the quality, not just quantity.
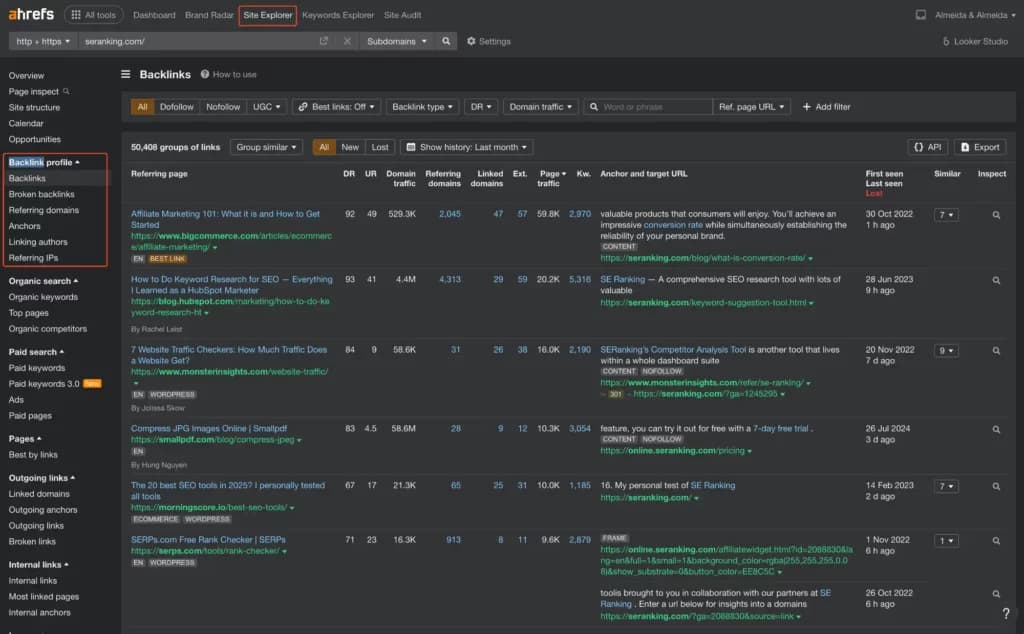
- Find Common Linkers: Identify websites that link to multiple competitors but not to you. These are prime targets for your own link-building outreach. They’re clearly interested in your niche. Here you want to use the link intersect tool.
- Analyze Link Velocity: Are competitors consistently earning new links, or is their profile stagnant? Use the calendar tool for this.
- Examine Top Linked Pages: Which specific pages on their site attract the most links? This often correlates with their best content.
- Look at Anchor Text: What words are used in the links pointing to their site? Is it branded (“Competitor Inc.”), keyword-rich (“best running shoes”), or generic (“click here”)?
Action: Build a list of high-quality, relevant websites linking to your competitors (especially those linking to multiple). Use this list to inform your link-building campaigns. Aim to acquire links from similar or better sources.
Step 6: Advanced: Competitor Intent Mapping
This takes keyword analysis a step further. It’s about understanding the why behind the search query your competitor is ranking for and matching your content accordingly.
The Process:
- Identify Top Keywords (Again): Look at a competitor’s high-ranking keyword.
- Analyze the Ranking Page: Go to the page that ranks for that keyword.
- Determine the Search Intent: Why would someone search for that term? Are they looking for:
- Informational: To learn something (“how does photosynthesis work?”)
- Navigational: To find a specific website (“facebook login”)
- Transactional: To buy something (“buy nike air force 1”)
- Commercial Investigation: To compare products/services before buying (“best crm software”)
- Evaluate Content Alignment: Does the competitor’s page effectively satisfy that intent? Is it an in-depth guide (informational), a product page (transactional), or a comparison list (commercial)?
- Compare with Your Content (or Lack Thereof): Do you have content targeting that keyword? Does your content match the likely search intent as well as or better than the competitor’s?
Here you have to execute #1 and #2 manually, if you don’t use automation for this, and points #3, #4, and #5 can be executed with the help of AI. Here’s the prompt:
Just input the two URLs or the two markdown files.
Action: For your most important target keywords, map the likely search intent and analyze how well your competitors’ ranking pages meet that intent. Ensure your own content strategy aligns perfectly with user intent for the keywords you target.
Step 7: Automate Competitor Monitoring & Reporting
SEO competitor analysis isn’t a one-time task. The digital landscape changes constantly. Competitors launch new content, earn new links, and change their strategies. You need to stay updated.
How to Automate:
- Rank Tracking Tools: Use tools (Semrush Position Tracking, Ahrefs Rank Tracker, SERPWatcher) to monitor your rankings and your competitors’ rankings for your target keywords. Set up automated reports (daily or weekly).
- New Backlink Alerts: Configure alerts in backlink tools to notify you whenever a competitor earns a significant new backlink. This can reveal new link-building tactics or opportunities.
- New Content Alerts: Some tools or services (like Google Alerts, although it can be noisy) can notify you when competitors publish new content mentioning specific keywords or on specific topics.
- Brand Mention Monitoring: Track mentions of your competitors’ brands online to understand their PR and brand-building efforts.
Action: Set up automated tracking and alerts for your top 3-5 competitors focusing on keyword rankings, new backlinks, and potentially new content. Schedule regular (e.g., monthly) reviews of these reports.
Real-World SEO Competitor Analysis Case Studies
Theory is great, but let’s see how this plays out.
E-commerce Example: Outranking Industry Giants
- Scenario: A small online store selling unique, handmade jewelry struggled to compete with huge retailers like Etsy and Amazon for broad keywords.
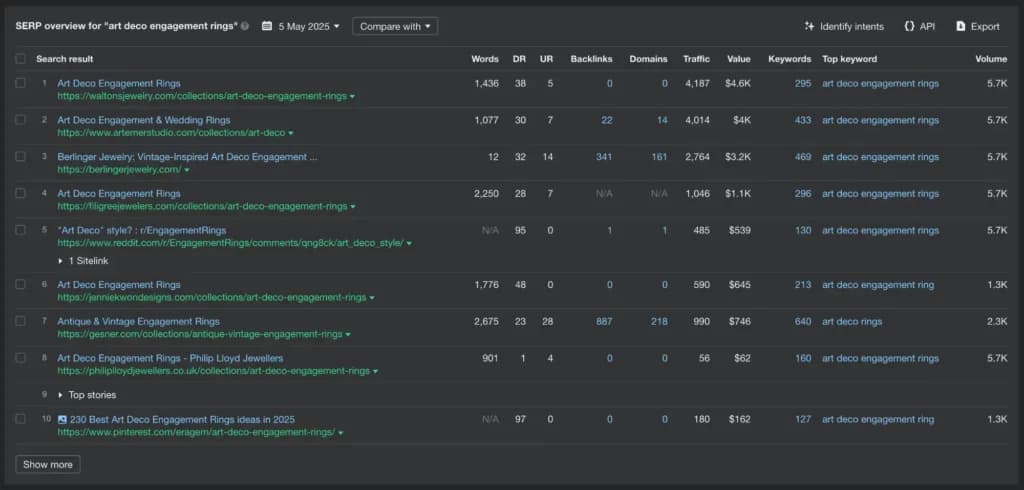
- Analysis: They performed a competitor keyword analysis and seo content gap analysis. They found the giants ranked for high-volume terms but often lacked in-depth content on specific niches (e.g., “art deco engagement rings,” “history of turquoise jewelry”). They also noticed competitors had few backlinks from niche craft blogs.
- Action: They focused on creating highly detailed blog posts and guides targeting these long-tail, informational keywords. They conducted backlink competitor analysis to find relevant craft blogs the giants ignored and secured guest posts and features, earning valuable niche backlinks.
- Result: While not outranking Amazon for “jewelry,” they carved out top rankings for valuable long-tail terms, driving qualified traffic that converted well, significantly growing their niche business.
SaaS Example: Winning with Technical SEO
- Scenario: A new SaaS startup offering project management software faced established players with massive marketing budgets and content libraries.
- Analysis: Competitor analysis revealed that while competitors had strong content and backlinks, their websites were often slow and clunky, especially on mobile (poor Core Web Vitals). A technical seo audit highlighted this gap.
- Action: The startup prioritized building a lightning-fast, mobile-perfect website from day one. They focused heavily on technical SEO best practices, ensuring excellent Core Web Vitals scores, clean code, and fast load times using technical seo audit tools for benchmarking.
- Result: Google rewarded their superior technical performance and user experience. They started ranking surprisingly well for competitive keywords faster than expected, gaining early traction against slower, more established competitors, proving that technical excellence can be a powerful differentiator.
Choosing the Right Tools for Each Step: Feature Comparison
You don’t need every expensive tool, but some investment definitely helps speed things up.
| Step | Key Features Needed | Popular Paid Tools | Useful Free/Freemium Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Identify Competitors | Organic competitor identification, Keyword overlap | Semrush, Ahrefs, Moz, SpyFu | Google Search, TSH Free Keyword Research Tool |
| 2. Analyze Keywords | Keyword research, Ranking data, Keyword gap analysis | Semrush, Ahrefs, Moz Keyword Explorer | Google Keyword Planner, Google Search Console |
| 3. Uncover Content Gaps | Top pages/content analysis, Content gap features | Semrush, Ahrefs, BuzzSumo (content focus) | Manual SERP analysis, AnswerThePublic (ideas) |
| 4. Evaluate Technical SEO & UX | Site audit, Page speed test, Mobile-friendly test | Semrush Site Audit, Ahrefs Site Audit | Google PageSpeed Insights, Mobile-Friendly Test, TSH On-Page Checker |
| 5. Examine Backlinks | Backlink profile analysis, Referring domains, Link gap | Ahrefs, Moz Link Explorer, Semrush | Limited free versions of paid tools |
| 6. Competitor Intent Mapping | SERP analysis features, Keyword research tools | Semrush, Ahrefs (primarily manual analysis) | Google Search |
| 7. Automate Monitoring | Rank tracking, Backlink alerts, Scheduled reports | Semrush, Ahrefs, Moz Pro, SE Ranking | Google Alerts (limited) |
Key Takeaway: Ahrefs and Semrush are powerful all-in-one suites. Moz is strong on links and authority metrics. Free tools are great for starting but limited for deep, ongoing analysis. Pick based on your budget and needs.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Doing competitor analysis is good. Doing it wrong is a waste of time. Avoid these pitfalls:
Only looking at direct business competitors.
Fix: Focus on your search competitors – who actually ranks for your keywords.
Just copying competitors.
Fix: Analyze to understand why they succeed, then innovate and create something better, not identical.
Focusing only on keywords.
Fix: Analyze the full picture: keywords + content + backlinks + technical SEO + UX.
Ignoring search intent.
Fix: Ensure your content matches the likely reason someone is searching for that keyword.
Using unreliable or incomplete data.
Fix: Use reputable tools and cross-reference findings where possible. Understand tool limitations.
Analysis paralysis (all research, no action).
Fix: Turn insights into a concrete action plan with deadlines. Start with the highest-impact, lowest-effort tasks.
Doing it once and forgetting about it.
Fix: Schedule regular competitor check-ins (monthly or quarterly) and automate monitoring.
Actionable Templates & Automation Workflows
Stop drowning in data. Get organized.
- Simple Template Idea (Spreadsheet):
- Tab 1: Competitors: List your top 3-5 search competitors, their domains, and maybe a key strength/weakness.
- Tab 2: Keyword Gap: Columns for Keyword, Competitor 1 Rank, Competitor 2 Rank, Your Rank, Search Volume, Difficulty, Intent, Target URL (Your Page).
- Tab 3: Content Gap: Columns for Topic/Angle, Competitor URL(s), Your Existing URL (if any), Content Format, Opportunity/Action Needed.
- Tab 4: Backlink Targets: Columns for Target Domain (linking to competitors), Contact Info (if found), Outreach Status.
- Tab 5: Technical/UX Issues: Columns for Issue (e.g., Slow Page Speed), Competitor Example, Your Status, Action Needed.
- Automation Workflow:
- Set up Rank Tracking: In your chosen tool (e.g., Semrush), add your domain and top 3-5 competitors. Add your core target keywords. Schedule weekly PDF reports emailed to you.
- Set up Backlink Alerts: In Ahrefs/Semrush, configure alerts for your competitors’ domains to notify you of significant new links (e.g., DR > 30). Review these weekly/monthly.
- Schedule Reviews: Block 1-2 hours on your calendar monthly or quarterly to review the automated reports, manually check competitor content/site changes, update your spreadsheet template, and adjust your action plan.
The key is consistency and turning data into tasks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Let’s tackle some common questions head-on.
Final Thoughts: Leveraging Competitor Analysis for Sustainable SEO Success
Look, SEO competitor analysis isn’t about spying or stealing. It’s about smart reconnaissance. It’s about understanding the game you’re playing and using data to make better decisions.
By consistently analyzing what your search competitors are doing well (and poorly), you can:
- Find untapped keyword and content opportunities.
- Build a stronger backlink profile.
- Ensure your technical SEO and UX are up to par.
- Allocate your resources more effectively.
- Ultimately, claim more space on that coveted first page of Google.
Don’t treat this as just another task on your checklist. Make it a core, ongoing part of your SEO rhythm. Use the insights you gather not just to react, but to proactively build a stronger, more resilient online presence. Now, stop reading and start analyzing. Go get those rankings!